Offshoring Meaning: The Ultimate Guide To Understanding Offshoring And Its Impact
Offshoring meaning is a buzzword that has been making waves in the business world for years. But what exactly does it mean? Offshoring refers to the practice of companies relocating certain operations or services to another country, usually to cut costs or take advantage of specialized skills. Think of it like this: instead of doing the work locally, companies outsource it to places where labor is cheaper or more efficient. It’s not just about saving money—it’s about staying competitive in a global market. So, if you’ve ever wondered how offshoring works or why companies do it, stick around. We’re about to break it down for you in a way that’s easy to understand.
Now, before we dive deep into the nitty-gritty, let’s clear up one thing: offshoring isn’t just about moving jobs overseas. It’s a strategic decision that affects economies, businesses, and even everyday workers. Some people see it as a game-changer, while others view it as a threat. But the truth? It’s a bit of both. In this article, we’ll explore what offshoring really means, its benefits, drawbacks, and how it’s shaping the global economy.
One thing’s for sure: understanding offshoring meaning isn’t just for economists or business leaders. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or someone curious about the global job market, this topic has something for everyone. So grab a coffee, get comfy, and let’s jump into the world of offshoring!
Read also:Winnetka The Hidden Gem Youve Been Missing Out On
What is Offshoring? A Simple Breakdown
Alright, let’s start with the basics. Offshoring, in its simplest form, is when a company moves part of its operations to another country. This could include manufacturing, customer service, IT support, or even research and development. The key reason companies do this? Cost savings. Labor costs, taxes, and regulations can be significantly lower in other countries. For example, a tech company might move its software development team to India because engineers there are highly skilled but charge less than their counterparts in the U.S.
But offshoring isn’t just about money. Companies also do it to tap into specialized expertise, access new markets, or improve operational efficiency. Think of it as a way to level up their business while keeping costs in check. And hey, if they can find a place where the work gets done faster and better, why not?
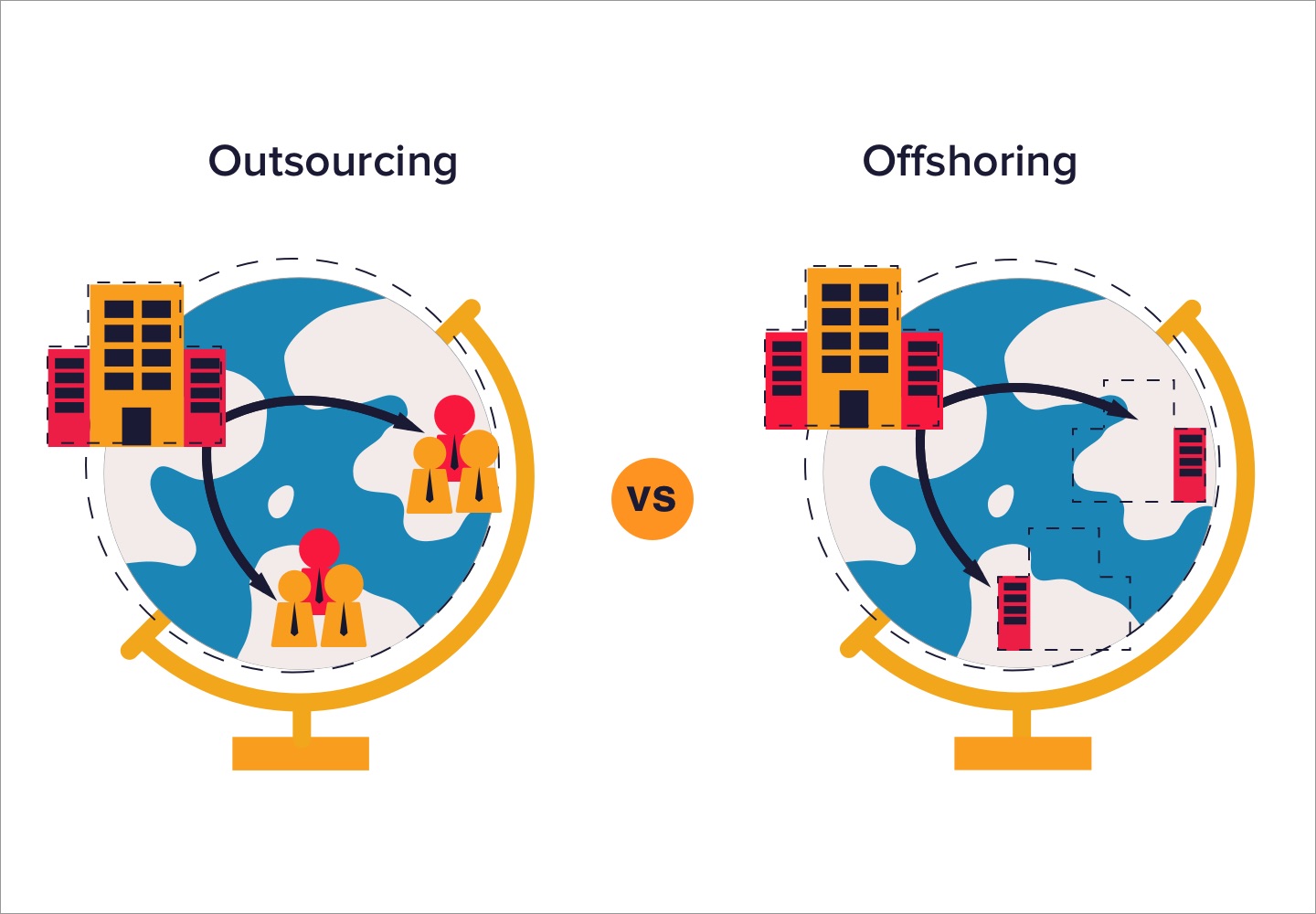
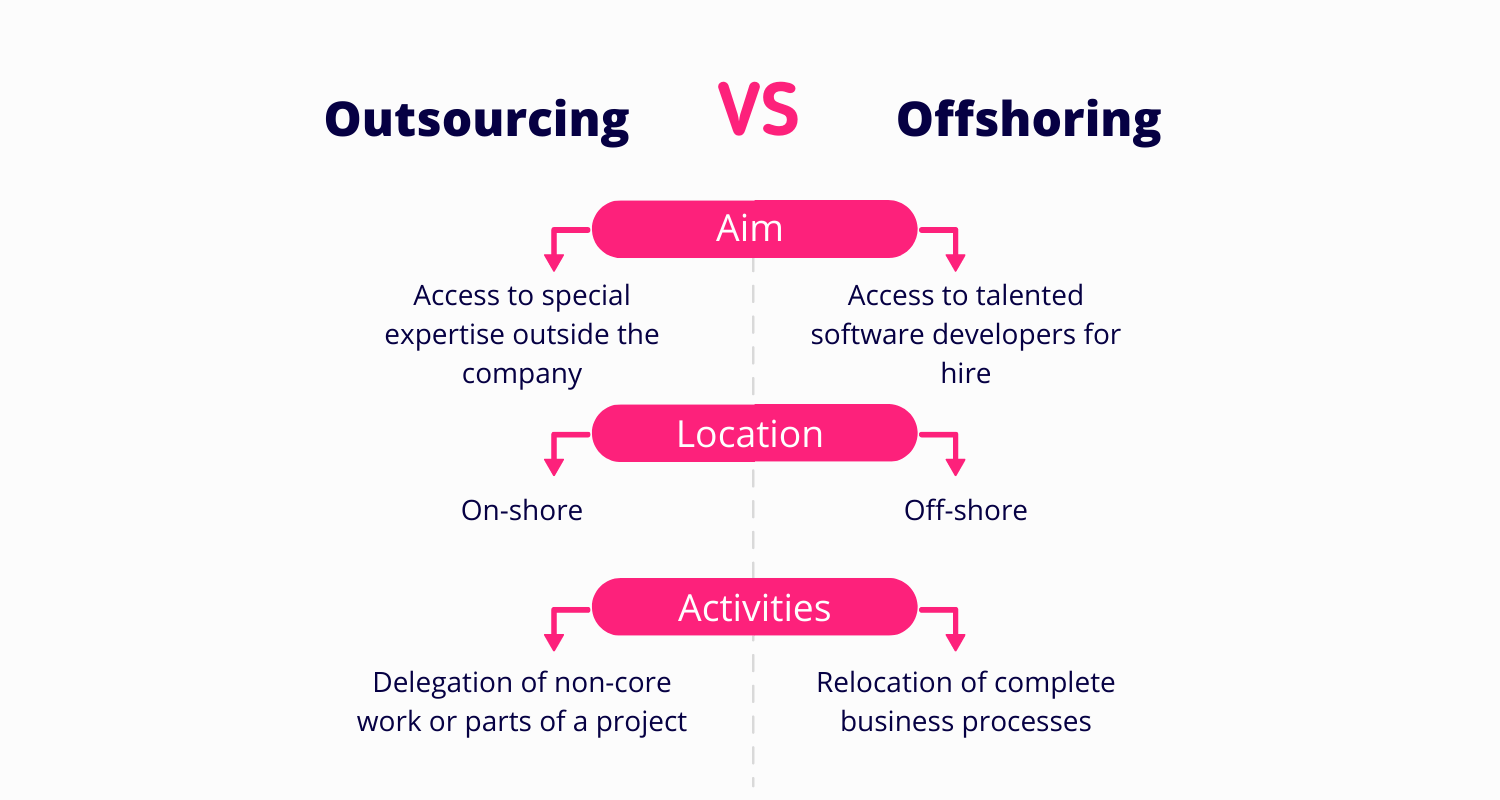
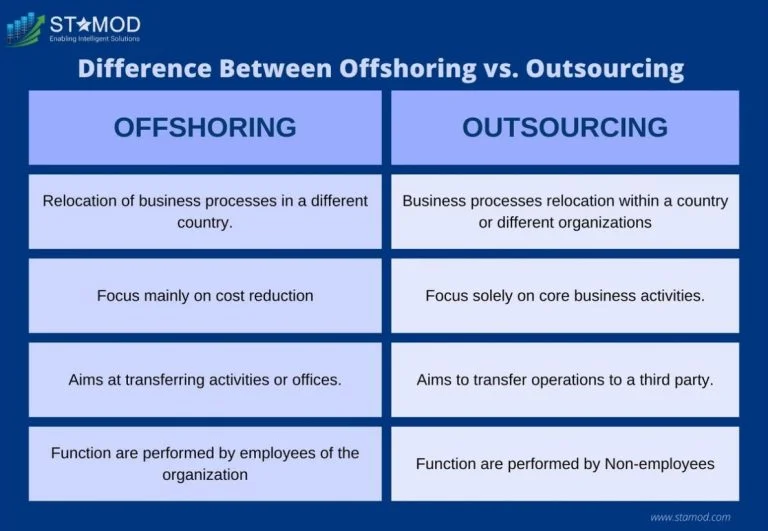
Offshoring vs Outsourcing: Are They the Same?
This is a common question, and the answer is: not exactly. While both involve moving work away from the company’s home base, they’re slightly different. Offshoring specifically refers to moving operations to another country, whether the company handles it internally or hires a third party. Outsourcing, on the other hand, means hiring an external company to handle the work, regardless of where it’s located.
For instance, if a U.S. company hires a Filipino call center to handle customer support, that’s offshoring because the work is being done overseas. But if the same company hires a local third-party firm to handle payroll, that’s outsourcing. See the difference? Offshoring is all about geography, while outsourcing is about who’s doing the work.
Why Do Companies Choose Offshoring?
Let’s face it: running a business isn’t cheap. From paying employees to dealing with regulatory compliance, costs can pile up quickly. That’s where offshoring comes in. By moving operations to countries with lower labor costs, companies can save big bucks. But cost savings aren’t the only reason. Here are some other factors that drive companies to offshore:
- Access to Skilled Labor: Some countries have a surplus of highly skilled workers in specific fields, like engineering or IT. Companies can tap into this talent pool without having to train their own employees.
- Operational Efficiency: Offshoring allows companies to focus on their core business while outsourcing non-essential tasks to experts in other countries.
- Market Expansion: By establishing operations in another country, companies can gain a foothold in that market and attract local customers.
- Regulatory Benefits: Some countries offer tax incentives or fewer regulations for foreign businesses, making it more attractive to set up shop there.
It’s not just about cutting corners. Offshoring can help companies grow, innovate, and stay competitive in a fast-paced global economy.
Read also:Vanessa Trump The Fascinating Life Story Of Donald Trumps Eldest Daughter
The Economics Behind Offshoring
From an economic perspective, offshoring makes sense for many businesses. According to a report by the McKinsey Global Institute, companies that offshore certain operations can reduce costs by up to 30%. That’s a pretty significant number, especially for large corporations with tight profit margins.
But it’s not just about the bottom line. Offshoring can also drive innovation. By collaborating with teams in different parts of the world, companies can gain fresh perspectives and ideas. For example, a U.S. tech company working with a team in India might discover new ways to solve problems or develop products that wouldn’t have been possible otherwise.
Benefits of Offshoring for Businesses
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s talk about the perks. Offshoring offers a ton of benefits for businesses, from cost savings to improved efficiency. Here are some of the top advantages:
1. Cost Savings
This one’s a no-brainer. Labor costs in countries like India, China, and the Philippines are significantly lower than in developed nations. For example, a software developer in the U.S. might earn $100,000 per year, while a similarly skilled developer in India might earn $30,000. That’s a huge difference, especially for companies with large teams.
2. Access to Global Talent
Not every country has a surplus of skilled workers in every field. By offshoring, companies can tap into a global talent pool and find the best people for the job, no matter where they are. This is especially important in industries like tech, where demand for skilled workers often outpaces supply.
3. 24/7 Operations
Offshoring allows companies to operate around the clock. For example, if a company has teams in the U.S., India, and Australia, they can have round-the-clock coverage for customer support or IT services. This can lead to faster response times and better service for customers.
4. Scalability
Offshoring makes it easier for companies to scale their operations up or down as needed. If demand increases, they can quickly hire more workers overseas without having to worry about building new facilities or training new employees locally.
Challenges and Criticisms of Offshoring
Of course, offshoring isn’t without its challenges. While it offers plenty of benefits, it also comes with some drawbacks that companies need to consider. Here are some of the biggest criticisms:
1. Job Losses in Home Countries
One of the biggest criticisms of offshoring is that it leads to job losses in the company’s home country. When companies move jobs overseas, local workers often lose out. This has sparked debates about whether offshoring is good or bad for the global economy.
2. Cultural and Communication Barriers
Working with teams in different countries can sometimes lead to misunderstandings or communication issues. Time zone differences, language barriers, and cultural differences can all make collaboration more difficult.
3. Quality Control
Offshoring can sometimes lead to quality issues if companies don’t properly manage their offshore teams. Without the right oversight, projects can fall behind schedule or fail to meet expectations.
Offshoring Meaning in Different Industries
Offshoring looks different depending on the industry. Let’s take a closer look at how it plays out in some key sectors:
1. Manufacturing
Manufacturing is one of the most common industries for offshoring. Companies often move production facilities to countries with lower labor costs, like China or Vietnam. This allows them to produce goods at a fraction of the cost while maintaining quality.
2. IT and Software Development
IT and software development are also big players in the offshoring game. Companies often hire offshore teams to handle tasks like coding, testing, and quality assurance. This not only saves money but also gives companies access to highly skilled developers in countries like India and Ukraine.
3. Customer Service
Customer service is another area where offshoring is common. Many companies hire offshore teams to handle tasks like answering phone calls, responding to emails, and resolving customer issues. This can lead to faster response times and lower costs for the company.
Offshoring Trends and Future Outlook
So, what’s the future of offshoring? As globalization continues to reshape the business landscape, offshoring is likely to become even more prevalent. Here are some trends to watch:
1. Rise of Remote Work
The pandemic accelerated the shift to remote work, making it easier for companies to hire workers from anywhere in the world. This could lead to more offshoring opportunities as companies realize they don’t need physical offices to get the job done.
2. Automation and AI
As technology advances, automation and AI are likely to play a bigger role in offshoring. Companies may use these tools to streamline operations and reduce the need for human labor, both locally and overseas.
3. Focus on Sustainability
With growing concerns about climate change, companies are under pressure to adopt more sustainable practices. This could affect offshoring decisions, as companies weigh the environmental impact of moving operations overseas against the cost savings.
How Offshoring Affects the Global Economy
Offshoring doesn’t just affect individual companies—it has a ripple effect on the global economy. Here’s how:
1. Economic Growth in Developing Countries
Offshoring has been a major driver of economic growth in developing countries. By bringing in foreign investment and creating jobs, it helps boost local economies and improve living standards.
2. Trade Imbalances
On the flip side, offshoring can contribute to trade imbalances between countries. When companies move jobs overseas, they often import goods and services back to their home countries, leading to trade deficits.
3. Skill Development
Offshoring can also drive skill development in both home and host countries. Companies that offshore operations often invest in training programs to ensure their offshore teams have the skills they need to succeed.
Conclusion: Is Offshoring Right for Your Business?
So, there you have it—a comprehensive look at offshoring meaning and its impact on businesses and the global economy. While offshoring offers plenty of benefits, it’s not without its challenges. Companies need to carefully weigh the pros and cons before making the decision to offshore.
If you’re considering offshoring for your business, here’s what you need to do:
- Identify which operations can be offshored without affecting quality or efficiency.
- Research potential host countries and assess their labor costs, skills, and regulations.
- Develop a clear strategy for managing offshore teams and ensuring smooth communication.
And hey, don’t forget to leave a comment or share this article if you found it helpful. Offshoring might not be for everyone, but understanding it is key to staying competitive in today’s global market. So, what do you think? Is offshoring the right move for your business?
Thanks for reading, and remember: the world is your oyster when it comes to offshoring!
Table of Contents
- What is Offshoring? A Simple Breakdown
- Offshoring vs Outsourcing: Are They the Same?
- Why Do Companies Choose Offshoring?
- The Economics Behind Offshoring
- Benefits of Offshoring for Businesses
- Cost Savings
- Access to Global Talent
- Challenges and Criticisms of Offshoring
- Job Losses in Home Countries
- Offshoring Meaning in Different Industries
- Offshoring Trends and Future Outlook
Article Recommendations